Two-Tier Collapsed Core Architecture
With the purpose to minimize the cost of devices and deployment while maintaining most of the benefits of the three-tier hierarchical internetworking model, the core layer and the distribution layer are collapsed into one layer, implementing the functions of two layers in a single device. Such type of design is called “collapsed core”. Reducing the three layers to two layers makes it possible to ease the burden of management and also makes it easier to troubleshoot network performance problems of the fewer hardware devices. Generally, the two-tier internetworking model is seen in the small-sized enterprise networks in which there are fewer than 200 users.
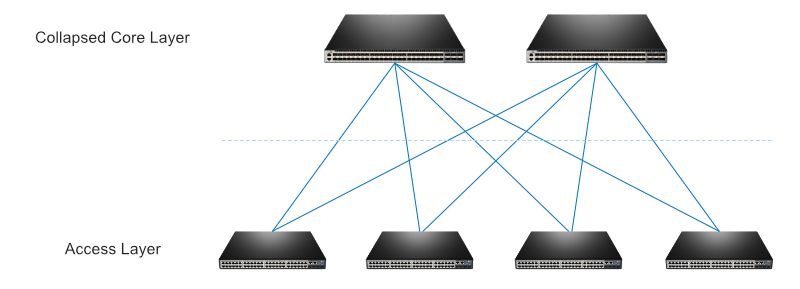
Figure 1: Two-tier collapsed core architecture
Distribution Switches in Three-Tier Architecture
In mid-sized to large enterprises comprising over 200 users, two-tier architecture is no longer available for the high requirement of network performance and availability. The traditional three-tier hierarchical network design comes to the stage and plays its role.
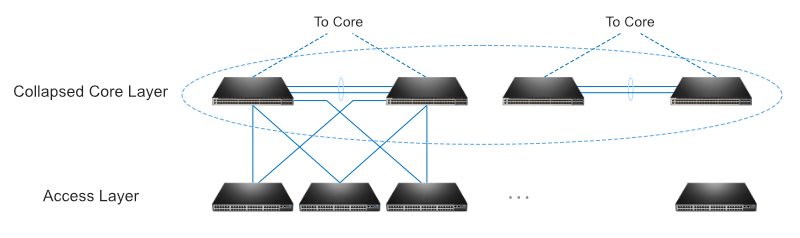
Figure 2: Distribution layer in a three-tier architecture
In the three-tier hierarchical network design, the distribution layer switches connect the core layer and access layer in an enterprise, functioning as a bridge so all the traffic to and from the access layer can flow into high-bandwidth trunk ports, and then the data is smoothly transmitted to the core layer for routing to its final destination. Besides the role of the connection point of the multiple access switches, distribution switches also play the role of terminating VLANs from the access switches, summarizing routing to access layer and so on.
Overall, whether to use the three-tier enterprise network architecture or two-tier collapsed core architecture depends on the type of the network and the potential future scale. If you are to build midsize and large enterprise networks with a larger amount of users, the two-tier collapsed core design is not a well designed one. Considering the cost and management, it is common to use two-tier design in a small-sized business network, but one cannot rule out the high potential to grow in size. In this case, network designers should take potential growth into account for future requirements. If network growth is possible, the three-tier enterprise network architecture is recommended.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Distribution Switches
No matter in two-tier collapsed or three-tier enterprise network architecture, you should make it clear what functions you require for the distribution switches in the collapsed core layer or distribution layer. With the general factors such as port type, port density and port speed considered, the following section will focus on the switch forwarding rate and functions that the distribution layer requires. Here are the factors for reference.
Layer 3 Function
It is always the responsibility of distribution switches to process Layer 3 data. The traffic generated from the access layer devices needs to be segmented into VLANs, requiring the upper-class switches to provide inter-VLAN routing functions so as to enable the multiple VLANs to communicate with each other. Since the core layer has a heavy task to handle the forwarding of the extremely high volumes of traffic, distribution switches with Layer 3 functionality are deployed to ease the workload of the core switches.
Forwarding Rate
The forwarding rate embodies the processing capabilities of a switch in the form of the data number that a switch process per second. It is a critical factor to consider when choosing a distribution switch. It is often the case that the forwarding rate of distribution switches is higher than the access switches. If the packet forwarding rate is too low, the distribution switch will not accommodate full wire-speed communication.
Redundancy
Redundancy is an important issue to consider for distribution switches. It is suggested that distribution switches should support multiple and hot swapping power supplies so as to achieve higher availability. With the redundant power supplies, the distribution switches can still operate normally without affecting the network traffic even if one power supply fails. In the meantime, the power supply can be replaced with a new one while the other one keeps operating as usual.
Link Aggregation
To forward all the traffic generated from the access layer to the core layer as fast as possible, distribution switches should support link aggregation so as to increase the network performance by keeping the traffic among a bunch of links balanced. Another key feature to use link aggregation is when a failure occurs, link aggregation will provide quick recovery. Generally speaking, link aggregation is an essential factor to take into consideration, which both increases availability and provides redundancy.
Security Policy
Security policy needs to be employed on the distribution layer switches to prevent promiscuous traffic through the network and allow others to go through. With the use of security policies such as access control list (ACL), the distribution switches can identify which types of traffic are permitted to communicate and which does not match the ACL rules defined on the switch ensuring the security of the whole enterprise network.
QoS Capacity
Setting up an intelligent QoS is essential for effective network capacity. As so many users sending traffic of various types within the LAN, deploying distribution switches with QoS features will read packets and prioritize delivery based on the policies so as to enable the important traffic to go first. It will ensure the audio and video data communicate in an adequate bandwidth. FS S5800-48F4S switches are well suited to the role of enterprise distribution switches supporting QoS capacities to improve the network traffic performance.